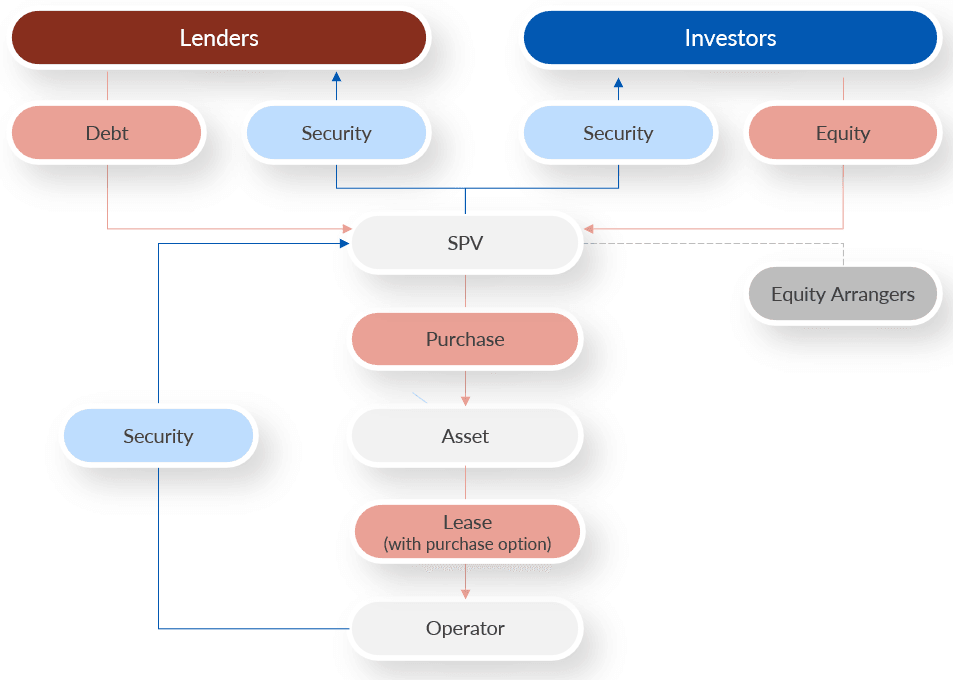
What is a Tokumei Kumiai structure?
Tokumei Kumiai structures, commonly known as TK structures, are a type of business arrangement that originated in Japan. TK structures are often used as a financing tool for real estate development and private equity transactions due to their flexibility, tax efficiency, and limited liability for investors. They have become increasingly popular in recent years, both in Japan and in other countries, as a way to structure investments and transactions in a tax-efficient manner.
In a TK structure, there are two types of partners: the operator and the silent partner. The operator, also known as the general partner, is the party responsible for managing the project or business. The silent partner, also known as the TK investor, provides capital for the venture but does not take an active role in its management.
One of the key features of a TK structure is that the silent partner has limited liability. This means that the TK investor's liability is limited to the amount of their investment in the venture, and they are not personally responsible for any debts or liabilities incurred by the operator.
In addition to limited liability, TK structures offer several other benefits. One of the primary advantages of a TK structure is its tax efficiency. In Japan, income earned through a TK structure is treated as capital gains, which are taxed at a lower rate than regular income. Additionally, the TK investor can offset losses from the investment against other income to reduce their tax liability.
Another advantage of a TK structure is its flexibility. The terms of the arrangement can be tailored to meet the needs of the parties involved. For example, the operator can offer a preferred return to the TK investor or give them the option to convert their investment into equity in the venture. The structure also allows for varying levels of involvement by the silent partner, depending on the nature of the venture and the preferences of the parties involved.
Despite its advantages, TK structures are not without their drawbacks. For example, the TK investor may have limited access to additional capital from the operator once the initial investment has been made. Additionally, the structure can be complex and difficult to set up, requiring the services of legal and financial professionals.
To establish a TK structure, the operator and the TK investor must enter into a partnership agreement that outlines the terms of the arrangement. The agreement typically includes details such as the investment amount, the expected return on investment, the duration of the partnership, and the roles and responsibilities of each partner.
In Japan, TK structures are subject to certain regulations under the Civil Code and the Commercial Code. For example, the TK investor must make their investment in cash, and the partnership agreement must be in writing. Additionally, the operator must provide regular financial reports to the TK investor. TK structures are a popular financing tool in Japan, particularly in the real estate and private equity sectors. However, they are also used in other industries, such as renewable energy, where they offer a way to structure investments and transactions in a tax-efficient manner. While the structure can be complex, it offers several benefits to both the operator and the TK investor, including limited liability, tax efficiency, and flexibility.
--end--