What is a JOL?
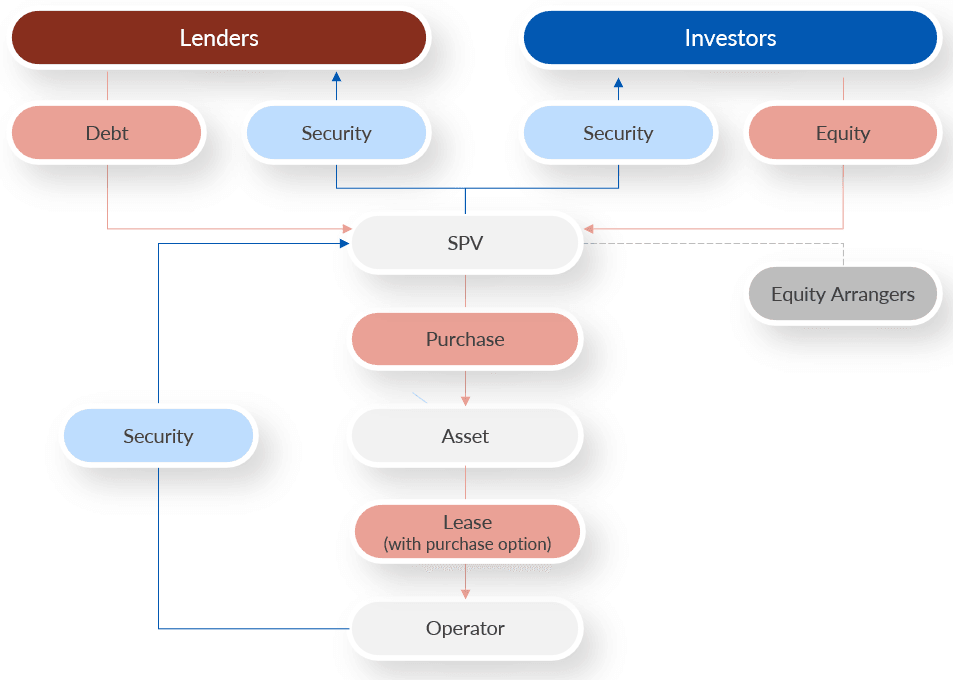
A Japanese Operating Lease (JOL) is a type of lease arrangement that is used extensively in the aviation and shipping industries. It is a popular financing option in Japan, but it is not well known in other countries, including Australia. JOL is a unique form of leasing that allows a Japanese SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle) to hold an asset on behalf of a Japanese company and lease it to an operator for generating revenue.
The concept of JOL is simple. The Japanese SPV acquires the asset and leases it to the operator for a predetermined lease rate. The operator uses the asset to generate revenue and pays the lease cost to the SPV. The lease rate is calculated based on the expected return on the asset, and the operator has the potential to earn returns above the lease costs.
One of the key benefits of a JOL is the ability to structure the lease as an operating lease rather than a finance lease. Under Japanese tax laws, it is important to have an operating lease rather than a finance lease. This is because a finance lease may result in higher taxes, and it may also affect the ability of the operator to claim tax deductions on lease payments. Therefore, the arrangement is structured to ensure that it is accounted for as an operating lease.
However, in some cases, it may be important for the operator to account for the lease as a finance lease. For example, if the operator is planning to use the asset for a long period and wants to show it as an asset on their balance sheet, a finance lease may be more appropriate. In such cases, GASS has developed a proprietary methodology that allows the operator to account for a finance lease, while the Japanese investor can account for an operating lease.
JOL financing is commonly used in the aviation industry to finance the acquisition of aircraft. For example, a Japanese airline may use a JOL to acquire an aircraft, which is then leased to the airline for a fixed period. At the end of the lease period, the airline has the option to return the aircraft or purchase it at a predetermined price. JOL financing is also used in the shipping industry to finance the acquisition of ships.
One of the advantages of JOL financing is that it allows the operator to acquire an asset without having to make a large upfront investment. Instead, the operator can lease the asset and make lease payments over the lease period. This helps to preserve the operator's cash flow and allows them to allocate capital to other areas of their business.
Another advantage of JOL financing is that it allows the Japanese investor to diversify their investment portfolio and generate a stable income stream. By investing in assets that are leased to operators, the investor can earn a steady stream of lease payments and potentially earn returns above the lease costs.
However, like any other investment, JOL financing carries some risks. One of the risks is that the operator may default on lease payments, which may result in a loss of income for the Japanese investor. Additionally, the value of the asset may depreciate over time, which may affect the value of the lease payments. However, these risks can be mitigated through proper due diligence and risk management practices.
At the end of the lease period, the JOL contract can be closed out in one of two ways. The first option is for the operator to return the asset to the SPV. In this case, the SPV may sell the asset to another operator or use it for other purposes. The second option is for the operator to purchase the asset at a predetermined price. In this case, the SPV may use the proceeds from the sale to invest in other assets or distribute it to the Japanese investor.
In conclusion, JOL financing is a unique form of leasing that is used extensively in Japan, particularly in the aviation and shipping industries. It is fairly uncommon in Australia, however GASS is dedicated to bringing this alternative financing structure down under as it can lower costs for operators, unlock cash and improve profitability for operators.
--end--